The reactive data store for local-first apps.
Build blisteringly fast web apps that work both online and offline. Manage your state locally, synchronize it to the cloud when you need to, or even make it collaborative. But, most importantly... have fun building stuff again!
Manage key-value data, tabular data - or both - with optional schematization to model your app's data structures.
Flexibly reactive to reconciled updates, so you only spend rendering cycles on things that change.
Powerful query engine to select, join, filter, group, sort and paginate data - reactively - and without SQL.
Built-in indexing, metric aggregation, tabular relationships - and even an undo stack for your app state.
Manage key-value data, tabular data - or both - with optional schematization to model your app's data structures.
Flexibly reactive to reconciled updates, so you only spend rendering cycles on things that change.
Powerful query engine to select, join, filter, group, sort and paginate data - reactively - and without SQL.
Built-in indexing, metric aggregation, tabular relationships - and even an undo stack for your app state.
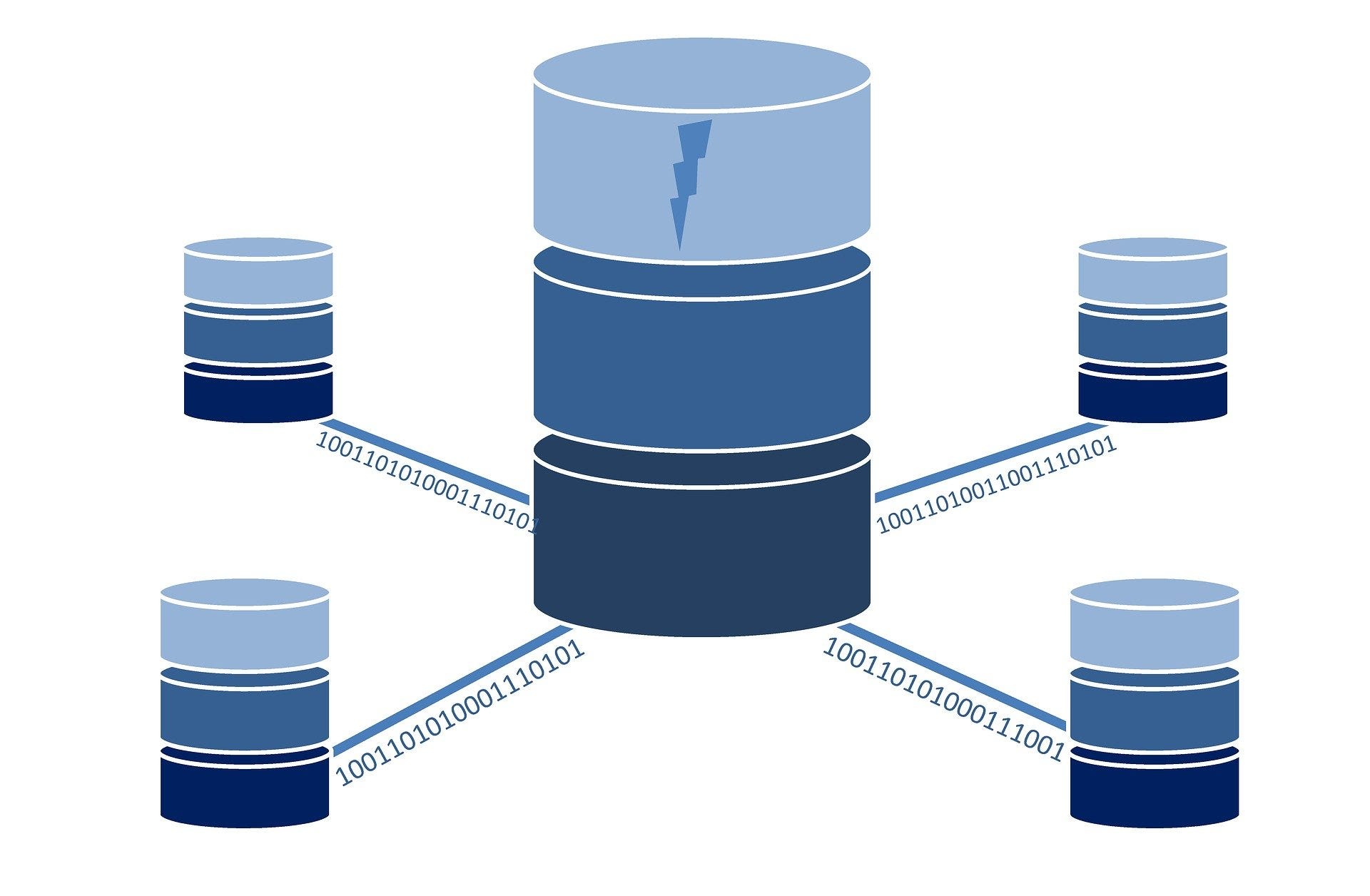
FrontQL works great on its own, but also plays well with friends!
React
PartyKit
Expo SQLite
ElectricSQL
SQLite
Turso
PowerSync
IndexedDB
YJS

CR-SQLite
Automerge


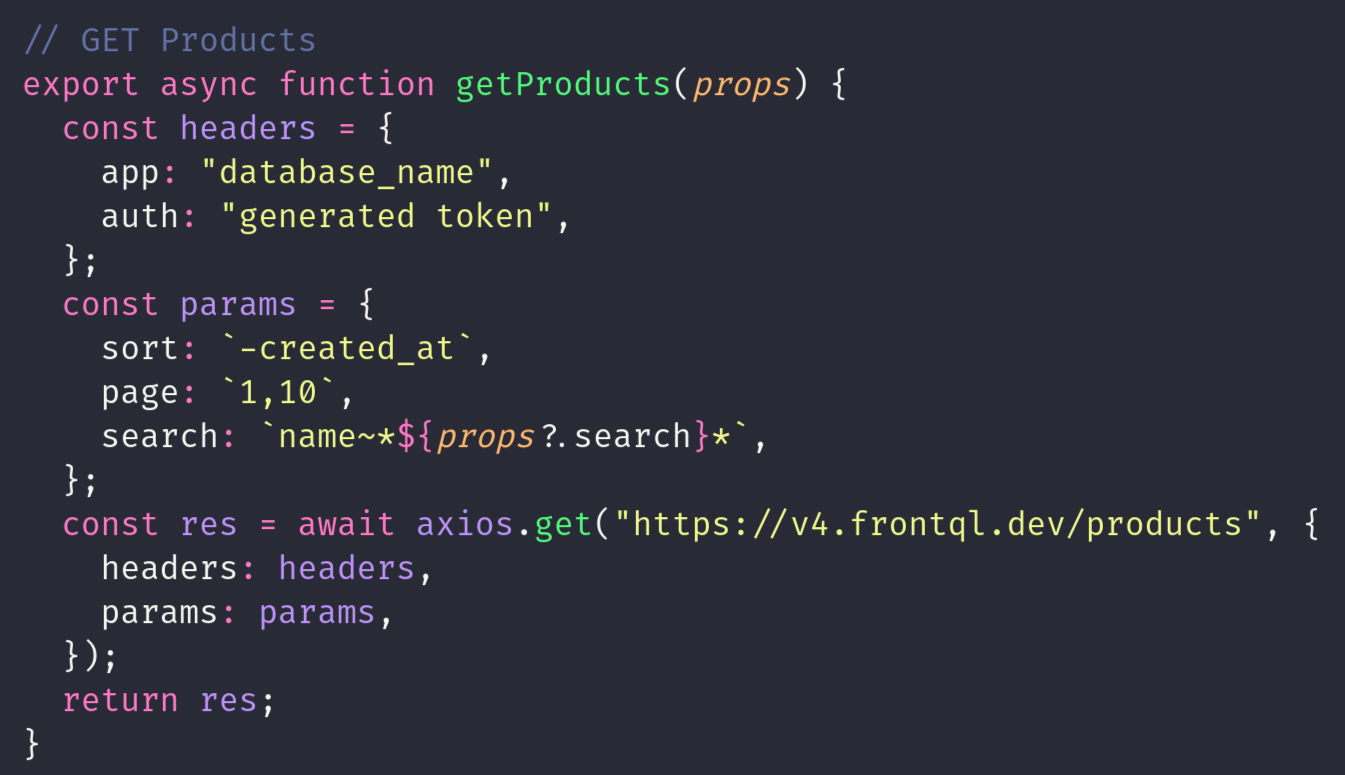
GET METHOD
The HTTP GET method retrieves a resource representation without modifying it. In the example frontql.dev/products, it fetches information about users from the server without altering their data. When a client sends a GET request to "baseurl/users", the server returns a representation of the users' data, such as their names, emails, or other details, depending on the implementation. This method is commonly used in web applications to display user profiles, lists, or any data stored in a structured format. It's an essential part of client-server communication for accessing information while ensuring data integrity.

POST METHOD
The HTTP POST method creates a new resource on the server. In the example "frontql.dev/products", sending a POST request with a body containing user data like {name:"Rishav"} results in creating a new user entry with the name "Rishav". This method allows clients to add data to the specified resource. The server processes the request, validates the data, and stores it according to the defined schema. POST requests are commonly used in web applications for user registration, form submissions, or any scenario requiring the addition of new data to a database or backend system.
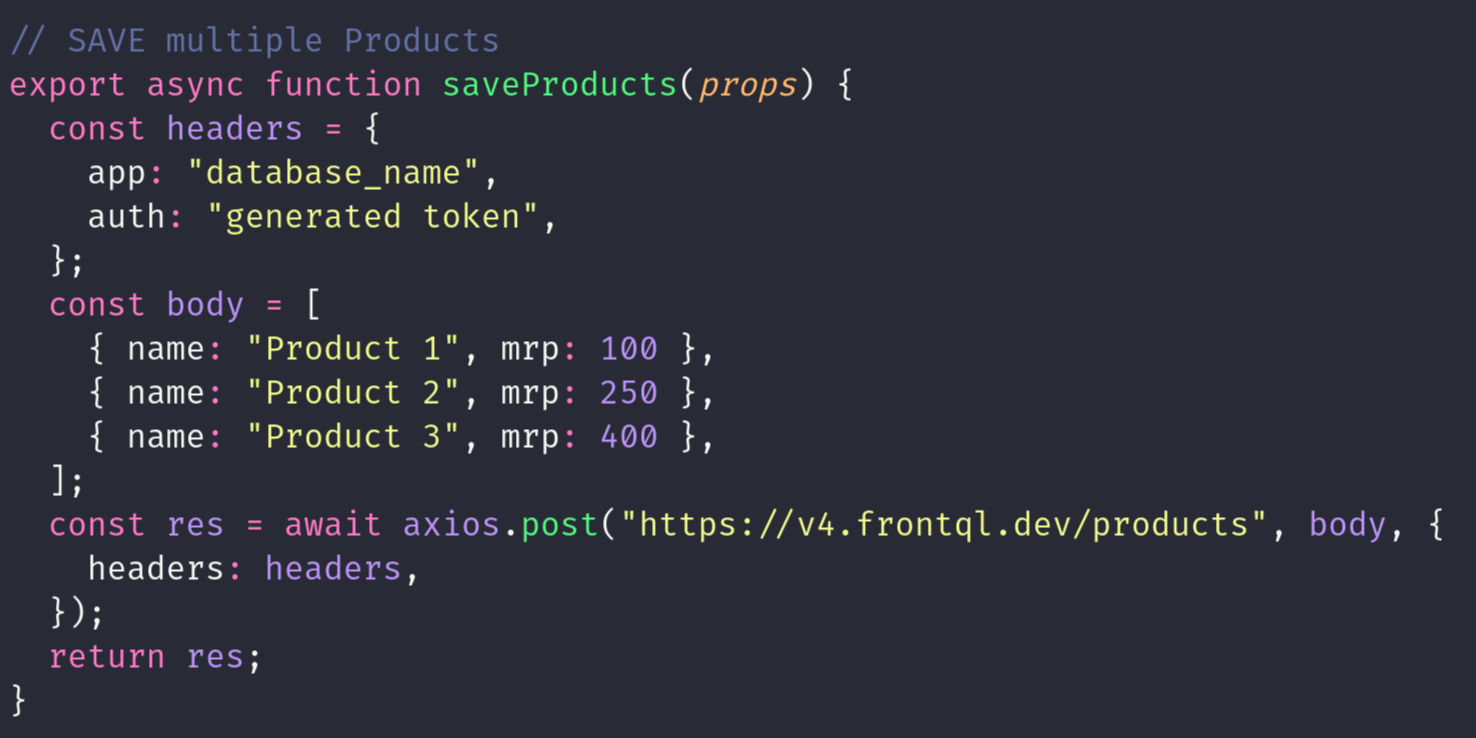
POST(Multiple Insert) METHOD
The HTTP POST method, with multiple insert capability, allows creation of several resources at once. For instance, posting to "frontql.dev/products" with a body containing an array of user data like [{name:"Rishav"}, {name:"Rishi"}], results in creating both "Rishav" and "Rishi" user entries. This method is efficient for bulk data insertion. When using raw SQL, the server processes the request, executing the provided query to insert multiple rows into the specified table. It's a powerful feature for applications needing to handle large amounts of data insertion in a single operation.
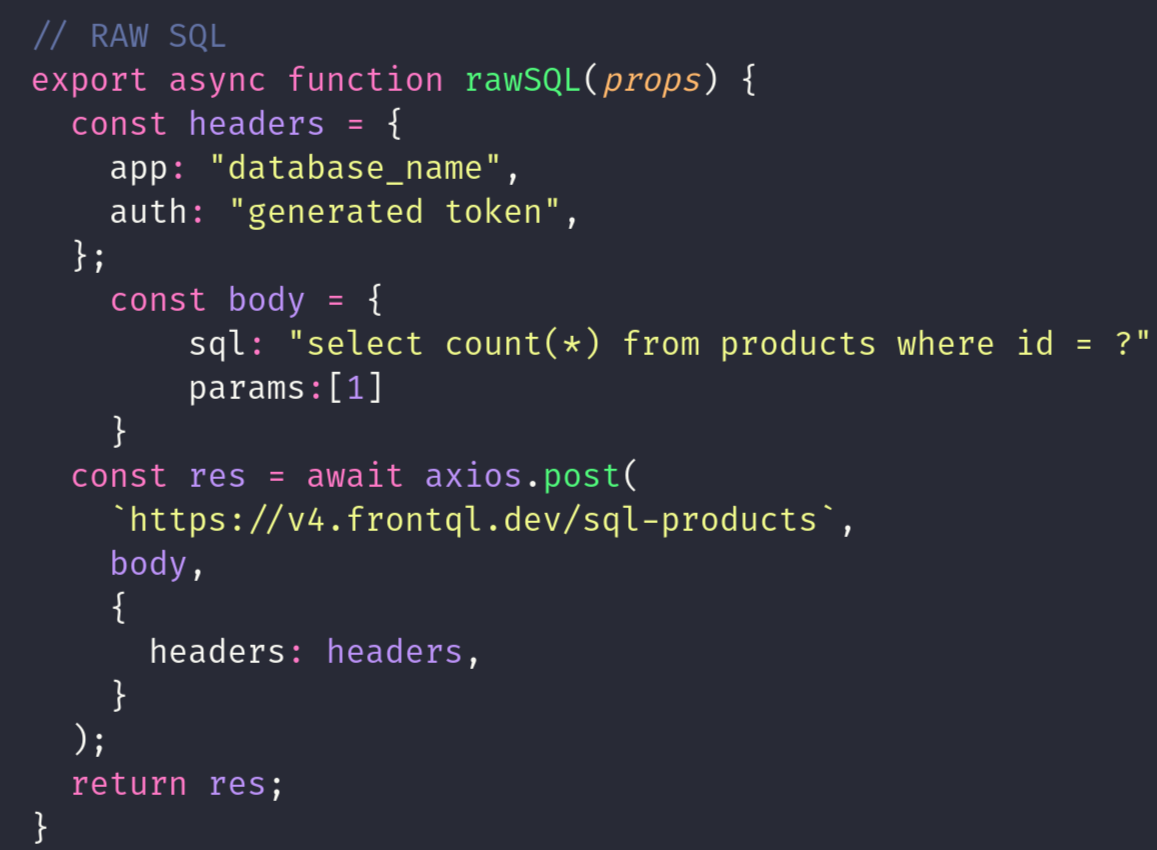
POST(RAW SQL) METHOD
The HTTP POST method with raw SQL allows executing custom SQL queries on the server. For instance, posting to "frontql.dev/products" with a body containing an array of SQL queries and optional parameters like [{sql:"SELECT * FROM USERS"}, {sql:"INSERT INTO USERS(name) VALUES(?)", params:['Rishav']}], executes these queries. This method is useful for applications requiring flexibility in database operations. The server processes the request, executes the provided SQL queries, and returns the results. It's commonly used in scenarios where ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) or other abstractions aren't sufficient for complex database interactions.
PUT METHOD
The HTTP PUT method updates an existing resource on the server. For example, sending a PUT request to "frontql.dev/products" with a body containing updated user data like {name:"Rishav"}, updates the user with ID 1 to have the name "Rishav". This method is crucial for modifying specific resource attributes. The server processes the request, validates the provided data, and applies the changes to the specified resource. PUT requests are commonly used in RESTful APIs to perform full updates to resources, ensuring consistency and accuracy in data management operations..
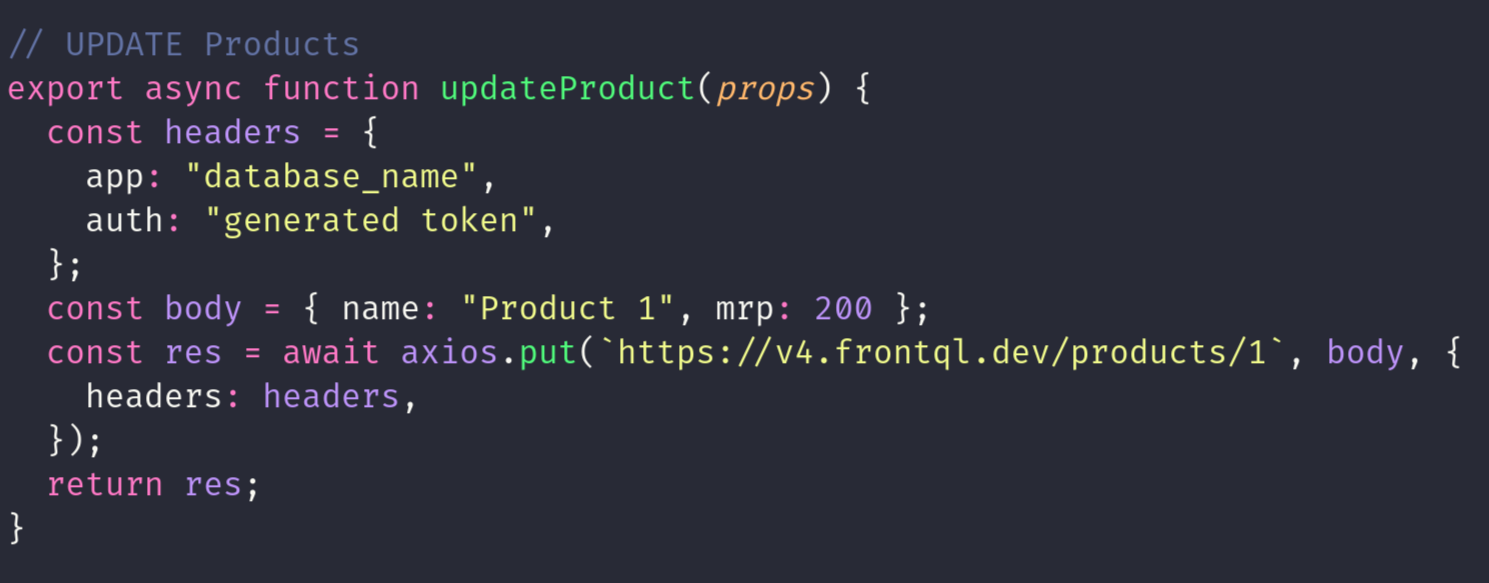
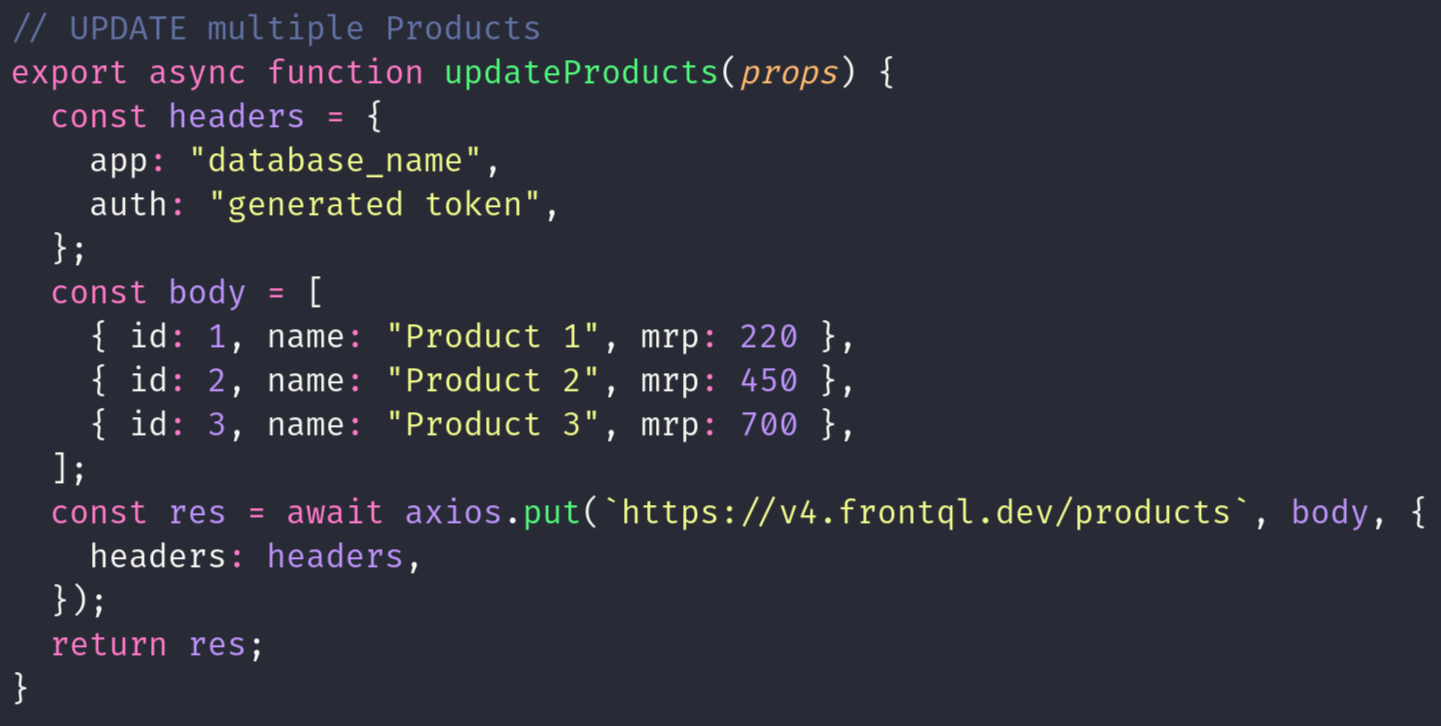
PUT(Multiple Update) MEHTOD
The HTTP PUT method with multiple updates enables modifying multiple resources simultaneously. For instance, a PUT request to "frontql.dev/products" with a body containing an array of objects specifying resource IDs and updated field data like [{id:1, name:"Rishav"}, {id:2, name:"Rishi"}], updates users with IDs 1 and 2 to have the names "Rishav" and "Rishi", respectively. This method efficiently handles bulk updates, crucial for applications needing to modify multiple resources in a single operation. The server processes the request, validates the provided data, and applies the changes to the specified resources, ensuring consistency across the system.
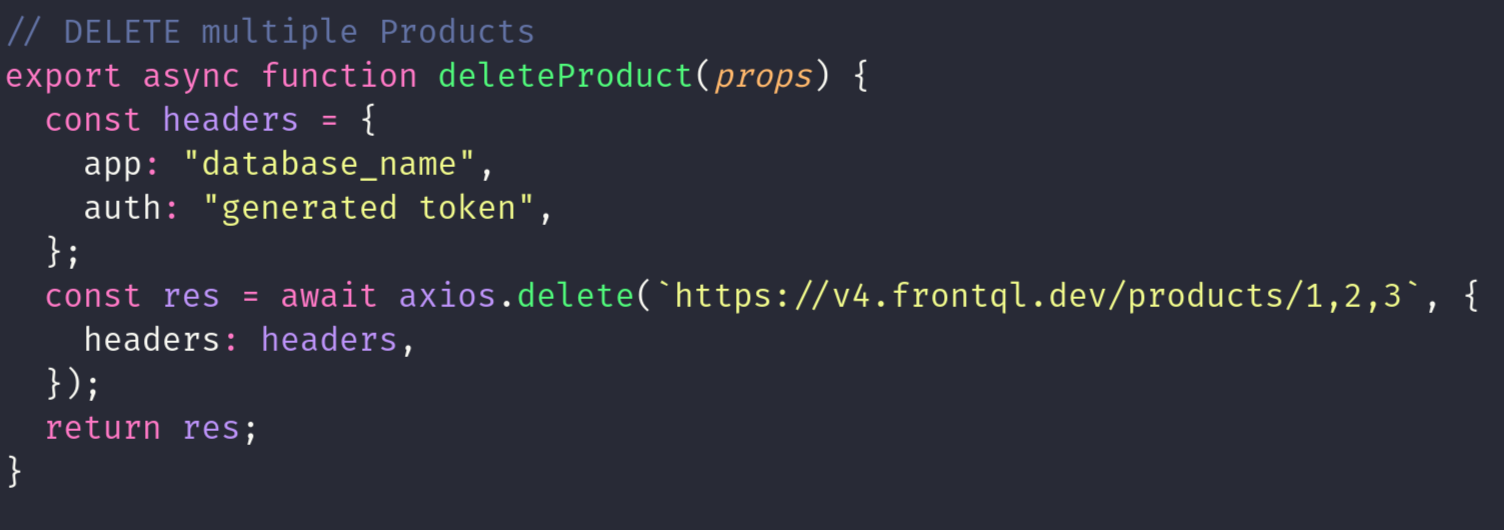
DELETE METHOD
The HTTP DELETE method removes a specific resource from the server. For example, sending a DELETE request to "frontql.dev/products" would delete the user with the corresponding ID from the system. This method is essential for managing data by allowing the removal of individual resources. Upon receiving the request, the server processes it and deletes the specified resource, ensuring data integrity and maintaining system cleanliness. DELETE requests are commonly used in RESTful APIs to enable clients to remove data entities when they are no longer needed or relevant.
About Us
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book.